Sufism Beliefs – Sufism, or Tasawwuf as it’s miles regarded inside the Muslim global, is a paranormal form of Sunni Islam whose members pursue a non-secular enjoyment using bodily area and mystical instinct. The sect also incorporates ecstatic stories and the adoration of Muslims “pirs,” or saints.
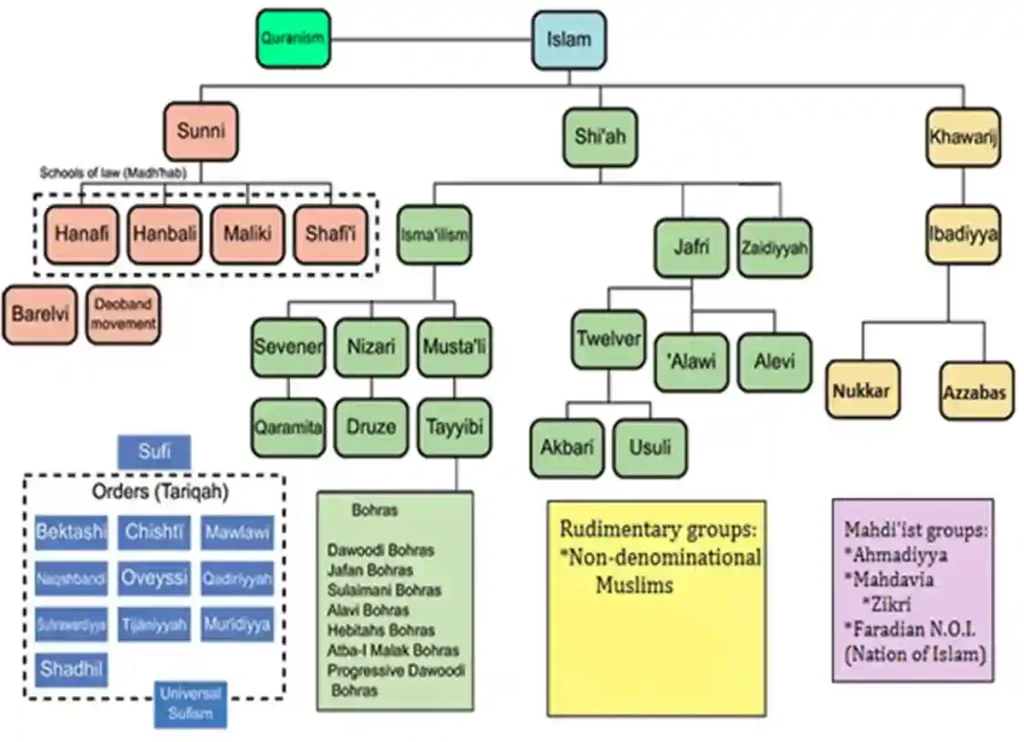
Non-Muslims regularly mistake Sufism as a sect of Islam. Sufism is more accurately described as a component or measurement of Islam. Sufi orders (Tariqas) may be discovered in Sunni, Shia, and Islamic companies.
The phrase Sufi comes from the Arabic for wool because early followers wore robes of coarse white wool. In medieval instances, Sufis were also known as dervishes (their Persian name) and fakirs, which imply “negative brother.”
Sufis are trying to find a near personal experience with God and agree that they have acquired a unique mystical knowledge directly from Allah.
Many Sufis outline their belief as a “religiosity” instead of religion as it revolves around personal revel instead of doctrine and entails contemplation, cognizance and a quest for purity.
The mysticism of Sufism is justified by passages from the Qur’an that describe the nearness of God and how humans can respond and at the mysterious nighttime adventure Muhammad made after he died to Jerusalem and Paradise.
Sufism turned into in no way a unified movement. Rather, it existed in separate colleges with their very own teachers, strategies, philosophies and beliefs.
Teachers, frequently known as Shaiks or Pirs, passed their methods down to disciples. Schools and sects that often have become centred across the tomb of the faculty’s founder have been formed. They normally have not been associated with any criminal faculty of ore other theological institution.
According to the BBC: “Although Sufis are pretty few in a wide variety, they have formed Islamic ideas and records. Through the centuries, Sufis contributed highly to Islamic literature.
For example, Rumi, Omar Khayyám and Al-Ghazali’s influence extended past Muslim lands to be quoted by Western philosophers, writers and theologians. Sufis had been influential in spreading Islam mainly to the furthest outposts of the Muslim international]
Conservative governments and Muslim extremists frequently oppose Sufism and regard Sufis as heretics. Even so, Sufi adepts are regularly more intense in their views and intolerance towards non-Muslims than typical Sunni Muslims.
Websites and Resources: Islam Islam.Com islam.Com; Islamic City islamicity.Com; Islam 101 islam101.Net; Wikipedia article Wikipedia; Religious Tolerance religioustolerance.Org/islam; BBC article bbc. Co.United kingdom/faith/religions/Islam;
Patheos Library – Islam patheos.Com/Library/Islam; University of Southern California Compendium of Muslim Texts internet.Archive.Org;
Encyclopædia Britannica article on Islam britannica.Com; Islam at Project Gutenberg gutenberg.Org; Islam from UCB Libraries GovPubs internet.Archive.Org; Muslims: PBS Frontline documentary pbs.Org frontline; Discover Islam dislam.Org ;
Shias, Sufis and Muslim Sects and Schools Divisions in Islam archive.Org ; Four Sunni Schools of Thought Masud.Co.United kingdom ; Wikipedia article on Shia Islam Wikipedia Shafaqna: International Shia News Agency shafaqna.Com ; Roshd.Org, a Shia Website roshd.Org/eng ;
The Shiapedia, a web Shia encyclopedia web.Archive.Org ; shiasource.Com ; Imam Al-Khoei Foundation (Twelver) al-khoei.Org ; Official Website of Nizari Ismaili (Ismaili) the.Ismaili ; Official Website of Alavi Bohra (Ismaili) alavibohra.Org ; The Institute of Ismaili Studies (Ismaili) net.Archive.Org ;
Wikipedia article on Sufism Wikipedia ; Sufism in the Oxford Encyclopedia of the Islamic World oxfordislamicstudies.Com ; Sufism, Sufis, and Sufi Orders – Sufism’s Many Paths islam.Uga.Edu/Sufism ; Afterhours Sufism Stories inspirationalstories.Com/sufism ;
Risala Roohi Sharif, translations (English and Urdu) of “The Book of Soul”, by using Hazrat Sultan Bahu, a 17th century Sufi risala-roohi.Tripod.Com ; The Spiritual Life in Islam:Sufism thewaytotruth.Org/sufism ; Sufism – an Inquiry sufismjournal.Org

Defining Sufism
Sufism Beliefs – The extremely good 14th-century Muslim pupil and historian Ibn Khaldun defined Sufism as: “determination to worship, total willpower to Allah maximum High, disregard for the finery and ornament of the arena, abstinence from the satisfaction, wealth, and status sought by using maximum men, and retiring from others to worship by myself.” [Source: Ibn Khaldun, quoted in Keller, Nuh Ha Mim, The Place of Tasawwuf in Traditional Islam, www.Masud.Co.Uk, 1995]
Arthur Goldschmidt, Jr. Wrote in “A Concise History of the Middle East”: Sufism is a tough problem to speak about. Any attempt to outline it’s far apt to mislead you. My attempt to do so is alternatively like calling the oyster “a sea creature with a grey shell.”
While many Muslims, whom I understand, scorn Sufism as a nonrational perversion of Islam, others make it the essence of their faith.
Many Sufis regard their ideals and practices as ordinary, current in every faith, and no extra (or much less) Islamic than Christian, Buddhist, or Zoroastrian. They are saying each religion incorporates the germ of closing reality; however, when controlled via an unsympathetic and worldly hierarchy, it can degenerate into a meaningless cult.
Sufism seeks to rediscover, meaning this is veiled from our senses and impenetrable to human reason. In monotheistic religions like Islam, locating the ultimate truth is called communion with God.
This can be carried out by way of meditation or via esoteric rites, along with prolonged fasting, night vigils, controlled respiration, repetition of phrases, or whirling for hours on one spot.”
Nicholas Schmidle wrote in Smithsonian Magazine: “Sufism is not a sect, like Shiism or Sunnism, however rather the paranormal side of Islam—a non-public, experiential technique to Allah, which contrasts with the prescriptive, doctrinal approach of fundamentalists like the Taliban.
It exists in the course of the Muslim global (perhaps maximum visibly in Turkey, where whirling dervishes represent a strain of Sufism), and its tens of millions of followers commonly embrace Islam as a non-secular enjoy, not a social or political one. Sufis constitute the strongest indigenous force against Islamic fundamentalism.
Yet Western international locations have tended to underestimate their significance at the same time as the West has spent, on account that 2001, thousands and thousands of greenbacks on interfaith dialogues, public diplomacy campaigns and other projects to counter extremism. Sufis are especially great in Pakistan, where Taliban-inspired gangs threaten the prevailing social, political and non-secular]
The Principles of Sufism, Book 23

Early History of Sufism
Sufism Beliefs – From the earliest days of Islam, a few Muslims were interested in mystical interpretations of their faith. The period Sufi derives from the Arabic suf, which means wool. Early Muslims used the period Sufi to refer to fellow believers who wore simple woollen clothes to illustrate their rejection of materialism and worldly temptations and their devotion to a lifestyle of asceticism and prayer.
Eventually, some Sufis who had acquired reputations for gaining knowledge of and piety attracted disciples who aspired to study from and emulate those Sufi masters.
Initially, Sufi fans have been like students whose bonds to a Sufi trainer have been primarily based on personal loyalty. Since the 12th century, most Sufis have prepared themselves into orders or brotherhoods that follow the lessons of a selected Sufi grasp. [Source: Library of Congress, January 1995 *]
According to the BBC: “Several origins of the phrase ‘sufi’ were recommended. It may also derive from the phrase for ‘wool’ and the woollen garments worn by early Sufis.
It might also connect with the word for ‘purity’, and every other inspiration is its hyperlinks with the Greek’ Sophia or know-how. However, during records, a Sufi becomes most customarily understood to be a person of spiritual learning who aspires to be near Allah.
They recognize their reason in life from the verse of the Qur’an; “I created the Jinns and humankind handiest that they’ll worship me.” —Quran fifty one:56 [Source: BBC, September 8, 2009, became based by using Islamic purists who had been disgusted with the materialism of Islam’s leaders and desired to have private enjoy with and direct touch with God beneath the steerage of teachers or masters.
Sufis have historically practised their esoteric beliefs personally, and that manner prevented the issues that Christians branded as heretics.
There was additionally the understanding that Sufi reports have been so non-public and unfathomable that nobody could recognize them, even supposing an attempt was made to explain them.
Sufism has its roots in the eighth century, while Christian asceticism was nearing its peak and Muslims who resented the materialism of the ruling Muslim elite had been attempting to get on the essence of Islam through dwelling absolutely like Christian priests, even though Islam has historically frowned upon monasticism, and having a direct relationship with God.
One of their goals turned into trying and replica the conditions wherein Muhammad obtained his revelations. Although Sufism became truly encouraged through acetic Christianity,
Gnosticism, Hermitic traditions or even Buddhism, it appears to be an outgrowth of acetic Islam that seems to have been encouraged using a worry of God, looking for oneness with God and an exploration of perceived mystical notions discovered in the Qur’an and within Islam.
As Sufism advanced, it was also inspired by the traditional animistic ideals of Turks and Berbers, Zoroastrianism of Persians and other neighbourhood ideals and superstitions.
Sufi Mysticism And Sexuality in Sufi Thought

Drunken Sufis and Poets
Sufism Beliefs – In the ninth century, mystics, who fasted and used rhythmic breathing to send themselves into ecstatic states, became called the “drunken Sufis.” Some of them claimed to have been wooed by Allah-like lovers. Others said they had made a perfect country of Islam using denying themselves.
A few were done for blasphemy. The “sober Sufis” who arrived on the scene briefly later provided that mature Sufis returned to the arena from the transcendence and lived like excellent Muslims in a humble experience.
The wonderful Persian student al-Ghazali (1058-1111) became a fantastic poet and articulate of Sufism. He also helped reconcile many esoteric Sufi beliefs with mainstream Islam and helped shield orthodox Islam from attacks by Greek-inspired philosophers.
He believed that Sufi mysticism provided distinct possibilities to discover God’s genuine knowledge of God. However, he emphasized that a few preparations became necessary to guide the seeker nicely. Sufis have, on the whole, been a fringe motion.
They took up the decision to shield Muslim sites from the Crusaders. The sect then became organized around brotherhoods and holy locations, frequently the tombs of the brotherhood founders. There turned into a secretive, spy-like first-rate to a number of the brotherhoods.
Later History of Sufism
Sufis won energy whilst rich people became fascinated through the moves and used their money to discover Sufi madrassahs and different establishments. Some had been quite huge and housed a huge quantity of followers.
In India, Central Asia and other parts of the Muslim globe, Sufis served as missionaries and have been key to the unfolding of Islam. They regularly had been able to win converts attracted by their claims as miracle people and their message of affection even as gambling down Islam’s inflexible beliefs and guidelines. In a few places, cell-like Sufi corporations infiltrated craft and trade groups inside the cities.
Arthur Goldschmidt, Jr. Wrote in “A Concise History of the Middle East”: “There was continually a detail of Sufism in Islam. However, it emerged as an awesome motion in the second century after the hijrah.
At first, it changed into a movement of ascetics, folks that sought spiritual exaltation by denying themselves the comforts of the flesh. Their riding force turned into a sturdy fear of God, but this evolved closer to a notion of the love of God.
Sufism may want to reduce the intellectualism of theology and soften the rigid legalism of “directly” Sunni (or Shi’i) Islam. It was not — s some modern-day writers think — a negation of the Shari’ah itself.
Sufism also approved Islam to bring in a number of the traditional practices of converts from different religions without adverse its vital doctrines. This facilitated its unfold to important Asia, Anatolia, southeastern Europe, India, Indonesia, and Black Africa.
“From the eleventh to the nineteenth century, Sufism dominated the religious existence of most Muslims. Brotherhoods of mystic dervishes, additionally referred to as Sufi orders, grew up during the ummah, providing a brand new basis for social cohesion. The Safavid dynasty, which dominated Iran between 1501 and 1736, began as a Sufi order.
Sufism also held together the warrior Ghazis, who based its better-recognized rival, the Ottoman Empire. The Safavids were Shi’is and the Ottomans Sunnis, which goes to show that both of the primary branches of Islam ought to accommodate Sufism. /~
As Sufism became increasingly famous and sizeable, it brought about back-to-fundamental moves among Muslim agencies along with Wahhabis that adversarial Sufism, arguing it was a superstition and insisting that Muslims go back to the primary doctrines of the early Islamic generation. In the 18th and 19th centuries, Sufis were persecuted and pushed underground.
Sufism | Definition & Sufism History
Sufism Beliefs
Sufis are searching for the truth of divine love and understanding through direct personal experience with God. They try and attain a country of “fana” (a transient ecstatic intoxication of divine love) and “baqa” (an extended condition of complete “human in-living with God”). Some Sufis viewed the excessive non-secular recognition as the “Light of Lights” and described the procedure of reaching it as “ascending tiers of illumination.”
Rather than focusing on the several guidelines and rules enumerated by way of the Qur’an, Sufism picks out poetic and mystic verses such as “Wherever you switch, there’s the face of God—”which additionally abounds” — and mines them for meaning.
Sufis have mapped out a paranormal theology that ambitions to search for our soul of God and feature a few specific spins given Islam. The Qur’an scripture about God being “toward man than his neck vein” turns into “I am near to reply the decision of the caller when he calls to me.”
Unlike mainstream Muslims, who regard the soul as a material substance related to the frame, Sufis regard the soul as something extra abstract and become independent from the body and connected to God, a belief that many Muslim recollect is blasphemous. For Sufis, Muhammad’s ascension to heaven appeared as a model for the flight of the human soul to God.
Sufis have laboured out their very own schemata of the universe. They had been closely encouraged by the thirteenth-century Persian sage Rumi who argued that earth, water, air and hearth are the simple factors and we are worth no greater than something we worry about, and a seeker of know-how is going thru many levels.
According to the Encyclopedia of World Religions, Sufis accept as true that: “the human spirit being a right away emanation from the divine Command, is therefore an emanation of God himself, and will locate its highest goal handiest in the obliteration of its illusory selfhood and absorption into the Eternal Reality. The excellent mystical enjoy is for this reason achieved in union with God, even if most effective momentarily.”
Sufi Brotherhoods
Since the twelfth century, maximum Sufis have organized themselves into orders or brotherhoods (tariqat; pl., tarikatlar) that comply with the teachings of a specific Sufi master. Many Sufi tarikatlar hooked up institutional bases, known as tekke or dargah (inns), that lasted for numerous generations and, in a few instances, even hundreds of years.
For instance, two of cutting-edge Turkey’s largest tarikatlar, the Naksibendi and the Kadiri, date returned at least to the fourteenth century. Some tarikatlar convey the name of the founding Sufi grasp, the seyh (in Arabic, shaykh). [Source: Library of Congress, January 1995 *]
One example is the Mevlevi Brotherhood. Its contributors are popularly referred to as whirling dervishes because of the rhythmic whirling they interact in as a spiritual exercise and a means to gain ecstatic proximity to God. The brotherhood is named after its founder, Mevlana (Jalal advert Din Rumi, d. 1273). Ordinarily, a designated successor to the seyh inherited his position of leadership in addition to the mantle of his non-secular strength.
Induction into a particular tariqat has become regulated and typically depends on the overall performance of prescribed initiation methods. Initiates have been positioned at unique levels, depending on the training they had mastered. Some of the larger Sufi tarikatlar established branches and, thru evkaf, accumulated land and buildings, which functioned as tekkes, Qur’an colleges, residential monasteries, orphanages, and hospices.*
The early tarikatlar have been strongly inspired by the aid of Shia doctrines. Consequently, the political conflicts between the Sunni Ottoman and Shia Safavi dynasties affected the Sufi orders in Turkey. Sunni tarikatlar, in the end, deemphasized such practices as the veneration of Ali ibn Abu Talib and acquired legit patronage from some Ottoman sultans.
However, at least one Shia tariqat, the Bektasi, supported the Ottomans and, in reality, exercised enormous political influence without converting their heterodox ideals.
The Bektasi and the Sunni tarikatlar additionally served a critical social function via imparting instructional and social welfare services, constituting a social mobility, and presenting non-secular steering to the people, particularly in rural regions.*
Sufi Masters, Holy Men and Structure
Many Sufi orders are organized around masters acknowledged in specific sects as “pir”, “sheik”, “ishan”, “murshid”, or “ustad”. Revered as instructors with divine connections to God, they offer steerage and non-secular assistance for fans and are a supply of thought.
According to a vintage Sufi saying: “he who has no sheik, the Devil is his sheik.” Many masters and teachers trace their lineage returned to pioneering instructors by way of the way “chains” of non-secular affiliations, which in flip are frequently linked to the Companions of Muhammad, regularly Ali.
Followers pass through exclusive stages of their religious journey. Sufi initiates are given a skullcap and black cloak. In the early stages of their quest, they have been now not unlike newly saved Christians, who introduced they might repent and promised to turn away from their sinful beyond.
The adventure regularly involved a development from the frame to strength to the spirit and a go back to the world that turned into now not in contrast to the route taken by Buddha.
Some Sufis are wandering dervishes who deliver a wooden cane and have hair tinted with henna. They travel from region to location and try to unfold the phrase of their faith; however, they need to be more elusive whilst speaking approximately themselves.
If you ask which Sufi ascetic wherein he goes comes from or how he earns his cash, he will say, “Only Allah knows.” Some are hermits who live in caves, like Buddhist or Hindu holy men. One Sufi grasp spent 50 years in the jungles of Sri Lanka, looking at animals and mastering God.
The shape of Sufism is extra hierarchal than orthodox Islam, which stresses the equality of all believers. Sufism became something that was found out. Initiates bypass via one-of-a-kind stages to become masters, with every better stage having a higher status.
In the past, masters developed a massive following and have become quite well-known. They acquired big amounts of money as presents, built big homes, and were revered with big shrines and treated as saints after they died. Muhammad discouraged this sort of adoration.
Sufism is enormously laid back in terms of policies and structure. On a few levels, Sufis reject spiritual hierarchy and stress direct human touch with the limitless.
Sufi sects are often decentralized and secretive. They often flout some of the Sharia rules, which puts them in a bad light in the eyes of conservative Muslims. A few Sufi sects aim to function inside the confines of the Qur’an and live near orthodox Islam.

Tariqas (Sufi Teachers)
According to the BBC: “Sufis are emphatic that Islamic expertise needs to be learned from teachers and now not exclusively from books. Tariqas can hint their teachers lower back via the generations to the Prophet himself. Modelling themselves on their teachers, college students wish they would glean something from the Prophetic person. [Source: BBC, September 8, 2009 goal of worshipping Allah, Sufis belong to Tariqas, or orders, mounted inside the first few centuries after the Prophet’s death.
These orders have a master who will teach sacred understanding to others inside the group. Although Tariqas have a long record, nowadays, a few Muslims have questioned the need for Tariqas, arguing that they had been alien to the Prophet himself.
Sufis make a powerful defence from the Qur’an and Sunna (what the Prophet said, did, agreed to or condemned). Well known that Tariqas had been no longer mounted at the time of the Prophet. They take into account that the Prophet, his companions, and their instant successors, the prior three generations, embodied Islamic mysticism;
however, the phenomenon turned too fashionable to have a specific name. Later generations of Muslims have become distracted by the aid of worldliness. So those, now inside the minority, that was dedicated to worshipping Allah have been given the name Sufi.
This flip of events became eloquently defined in the 10th Century via Abu l-Hasan Fushanji, who stated; Today, Sufism is a name without a fact. It changed into once a reality without a name. [Source: Abu l-Hasan Fushanji, quoted in Lings, Martin, What is Sufism?
The Islamic Texts Society, 1999, pg 45::phrase Sufism is absent from prophetic speech; it’s believed the Prophet describes Sufism’s area in Islam. Umar ibn al-Khattab, a companion of the Prophet, stated, “One day we have been sitting within the business enterprise of Allah’s Apostle (peace be upon him) while there seemed before us a person wearing natural white garments, his hair rather black.
There had been no signs of journey on him. None among us recognized him. At remaining, he sat with the Apostle (peace be upon him). He knelt earlier than him, placed his hands on his thighs, and stated: Muhammad, tell me about Islam.
“The Messenger of Allah (peace be upon him) said: Islam implies which you testify that there is no god however, Allah and that Muhammad is the messenger of Allah, and also you set up prayer, pay Zakat, have a look at the fast of Ramadan, and perform pilgrimage to the (House) if you are solvent sufficient (to undergo the rate of) the adventure. He (the inquirer) stated: You have informed the fact. [Source: Sahih Muslim, Book 1:Number 1]
“It amazed us that he could put the query and then he could himself confirm the reality. “He (the inquirer) stated: Inform me about Iman. “He (the Holy Prophet) replied: You affirm your faith in Allah, in His angels, in His Books, in His Apostles, inside the Day of Judgment, and you verify your religion in the Divine Decree about appropriate and evil. “He (the inquirer) stated: You have told the truth.
He once more stated: Inform me about Ihsan. “He (the Holy Prophet) said: That you worship Allah as if you are seeing Him, for though you don’t see Him, He, verily, sees you. “He (the enquirer) again said: Inform me about the hour (of the Doom).
“He (the Holy Prophet) remarked: One who’s asked knows no more than the only who’s inquiring (approximately it). ) “He (the inquirer) said: Tell me some of its symptoms. “He (the Holy Prophet) stated: That the slave-woman will supply start to her mistress and grasp, that you’ll locate barefooted, destitute goat-herds vying with each other within the production of astonishing buildings. )
“Then he (the inquirer) went on his manner; however, I stayed with him (the Holy Prophet) for a protracted whilst. He then stated to me: Umar, do you recognize who this inquirer turned into? I responded: Allah and His Apostle is aware of exceptional. He (the Holy Prophet) remarked: He turned into Gabriel (the angel). He came to you with a purpose to teach you in matters of religion.”
“In this famous hadith, the angel Gabriel asks about pivotal capabilities of the Islamic perception. They included Islam, Iman, and Ihsan. Islam is the outward practice of the religion. Iman is the perception of the unseen and what the prophets have informed us. Ihsan is to worship Allah as one sees him. Traditionally scholars have been able to educate every one of these vital parts of Islam.
The Imams of Sharia or ‘sacred law’ taught the extent of Islam. The Imams of Aqida or ‘tenets of religion’ taught Iman. The Imams of Sufism taught at the level of Ihsan. The need to examine a teacher is based on the Quranic verses; “Ask individuals who recognize if you realize no longer” — Qur’an sixteen: forty-three. “And follow the course of him who turns unto Me” — Qur’an 31:15
Sufi Sects
Sufism has never been unified. Different sects get up over extraordinary strategies used to reach various dreams. These covered poetry, tune, dance, meditation, chanting and trances. Over time exceptional colleges, brotherhoods and order evolved. Turkey is home to eleven important Sufi orders and some 400 sub-orders.
The principal Sufi schools, which date returned to the 12th century, are: 1) the Qadiriyya school (named after And- al-Qadiriyya, al-Gilan I of Baghdad, died 1166), that’s well represented in the Middle East.
Africa and the Caucasus; 2) the Melvini college (named after Jalal al-Din al-Rumi) located on the whole in Turkey; and 3) the Chishtiyaya ( from Mu’in al-Din Chishti of Sistan, died in 1236), primarily based in Pakistan, India and Southeast Asia There had been several suborders and small orders.
Sufi sects are frequently clandestine and decentralized. Some are fanatical. Some are ascetic. Many are concerned with assisting their groups, supporting the negative and teaching the young. In the old days, some were affiliated with craft guilds. Many Sufi sects do now not permit women to sign up for it.
The Naqshbandi (named Baha al-Din Naqshbandi, died 1389) sect is one every of the most important sects these days. It has followers all over the Muslim international today. Naqshbandi sect contributors perform “zikr”, wherein they recite the names of God and sacred verses even as doing breathing sporting events in unique postures and focusing their attention on particular components in their body. The sect persisted in Central Asia via the Soviet generation and reportedly turned by no means penetrated by using the KGB.
Text Sources: “World Religions” edited by way of Geoffrey Parrinder (Facts on File Publications, New York); “Encyclopedia of the World’s Religions” edited by using R.C. Zaehner (Barnes & Noble Books, 1959); Arab News, Jeddah; “Islam, a Short History” using Karen Armstrong;
“A History of the Arab Peoples” by Albert Hourani (Faber and Faber, 1991); “Encyclopedia of the World Cultures” edited by using David Levinson (G.K. Hall & Company, New York, 1994). Also, articles in National Geographic, the New York Times, Washington Post, Los Angeles Times, Smithsonian mag, Times of London, The New Yorker, Time, Newsweek, Reuters, AP, AFP, Lonely Planet Guides, Compton’s Encyclopedia and numerous books and other publications