Branches of Islam – It is believed that the Islam religion has more than 2 billion people who follow it around the world. The Islam religion itself is 1300 years old. The majority of Muslims consider that Islam began around 610 CE when the first prophet Muhammad was first receiving messages from God. The followers of the faith documented their revelations within the Qur’an.
Similar to other religions around the world, Islam is represented by various principal varieties: Sunni, Shi’a, Ibadi, Ahmadiyya, and Sufism. These branches first began to emerge after the death of Muhammad, when people started to argue about the future of Islam. While they are different, the main religions share a few common convictions about monotheism, holy scriptures and so on.
Suggested Read : How Many Chapters in Quran? ,la ilaha illa anta subhanaka, Has The Quran Been Changed?, How Many Pages in Quran? , Allahumma Ajirni Minan Naar, Allahu Mahdina, Allahu Alam , Allah Yashfeek , Allah Subhanahu Wa Ta’ala

The Major Denominations Of Islam
Sunni Sect
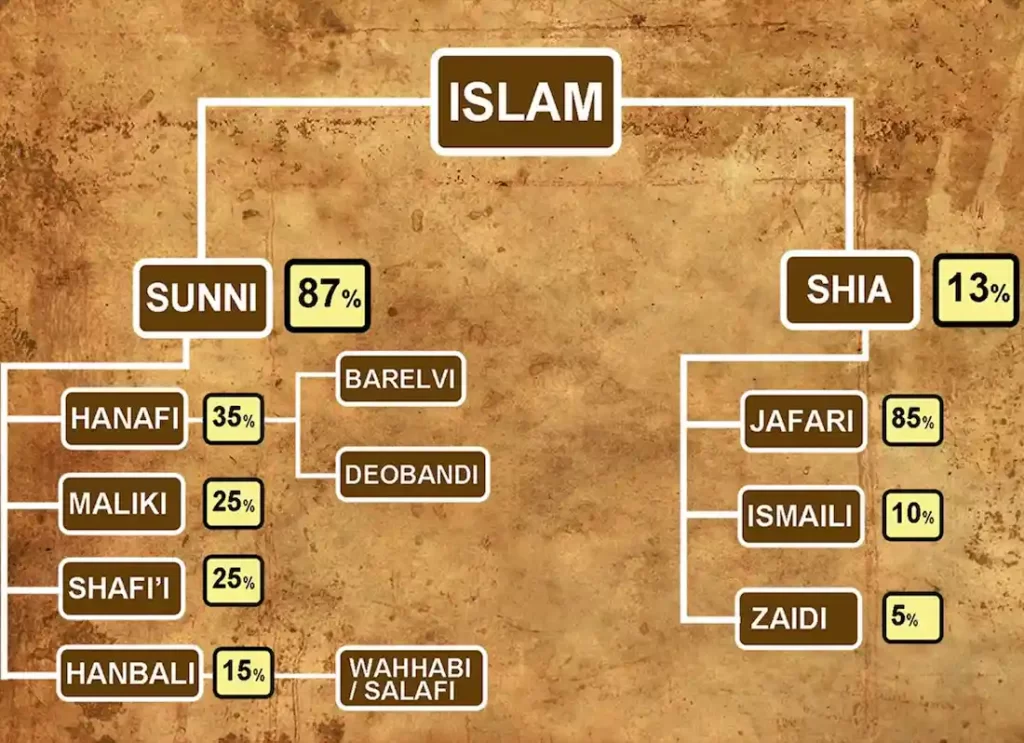
Branches of Islam – Sunni’s comprise the majority within Islam which makes around 85-90% of followers of the religion. The Sunni Islam has been dominant for a long time, since 661 which was the year that it was the time that Shi’is left the main group (the Kharijis were exiled at the time of 658). Sunni Islam asserts that it is the continuation of Islam in the sense that it was defined by the revelations by Muhammad as well as his own life.
This claim is supported by the evidence the Shi’i Islam for several years had a very small following and was not a official organization. In terms of religion, Sunni Islam represents no more than a continuation of Islam than other religious philosophies.
Sunni Islam has its name due to its association with the significance to the Sunna (the examples found in the hadiths) that prior to within Shi’i Islam was recognized as the key to the authentic picture of Islam. This was in connection with the need to establish an Islamic law, known as Shari’a – Seriat (for which the hadiths were an important source) in the sense that Sunni Islam was the religious direction of the rulers even though the Shi’is did not create administrative bodies for quite a while.
The real theological and spiritual differences in Sunni as well as Shi’i Islam, came over several centuries during advancement. For a long period, Sunni Islam was defined from Shi’i Islam by its adherence to the Caliph as the supreme leader in this Muslim globe.
There are many minor and more significant differences between Sunni and Shi’i styles in every aspect that are part of religion. Sunni is a Shi’i religion. Shi’i Islam share only three basic doctrines: the oneness of God and faith in revelations from Muhammad and the belief in the resurrection at the time of Judgment.
Sunni Islam has a different set of hadiths compared to Shi’i Islam. It is believed that in Sunni Islam, there are five prayers every day, whereas Shi’i Islam has only 3. Sunni Islam puts far more importance on prayers for the pilgrimage in Mecca as opposed to Shi’i Islam also has other major rituals too.
Sunni Islam is awed by Ali but doesn’t consider him to be as the sole true heir to the faith of Muhammad and does not place any importance on his bringing about the divine light of the Prophet. While Sunnis depend heavily on the teachings of Muhammad and the prophet’s instructions (the “Sunna”), Shi’is see the Ayatollahs they worship as reflections of God in the world of Earth.
The majority of population of Turkey comprise Sunni.
Suggested Read: The Islamic World by Ladan Akbarnia, Nahj al-Balagha by Imam Ali Ibn Abi Taleb, Lost Islamic History by Firas Alkhateeb, Stranger The History by Aatish Taseer, Prophet Muhammad (PBUH) by Abu Moosa Reza, Islamic Art by Luca Mozzati and Islamic History For Kids: Story of Uhud
Shi’i Sect
Branches of Islam – The biggest Non Sunni section in Islam is Shi’i in all their forms, constitute approximately 10-15 percent from all Muslim globe. The term”Shi’i” is used to refer to the supporters from the caliph of fourth Ali who was Muhammad’s son-in-law via his wife Fatima and was the final Caliph elected, and the last Caliph to be chosen from the first group of converts from the Mecca and Medina period.
The Shi’i in their diverse forms, constitute major minorities within Lebanon, Syria, Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Bahrain and in the Gulf States, Pakistan and India. They constitute the largest religion group in Iraq and the majority majority (88 percent) in Iran Shi’i Islam, which is the official religion since the 16th century AD.
The seeds of schisms were planted at the time of the demise of Muhammad the Prophet. Muhammad who according to Shi’i custom, he declared that Ali would succeed him as the chief of Islam. It turned out that it would take around 24-years before Ali became Caliph and, during the meantime, a significant number of partisans came together in the midst of this charismatic, driven man. Ali’s rule and election proved to be extremely turbulent, and he ended up being murdered in the fifth year of his rule.
After the assassination of Ali following a short period of chaos, the Caliphate was rebuilt under the administration of Mu’awiyaa. He created his own Ummawiyy dynasty. Mu’awiyaa’s regime brought many changes and the partisans from the past of Ali made up the basis that constituted the opposition. Ali’s oldest son Hasan was able to come to an agreement with Mu’awiyaa. However, it was only after his death and the rise of Ali’s daughter, Husayn to leadership of the Shi’i faction that the division was triggered.
Following the death of Mu’awiyaa the year 680 AD and hoping to prove an appeal to the caliphate Husayn fled Medina to Kufah. He was entrapped in the desert of Karbala by the troops of Yazid Mu’awiyaa, the son of Mu’awiya and the newly elected Caliph. In the absence of water and completely defeated, Husayn and his followers engaged in a bloody battle, and Husayn as well as his members were slaughtered. At this point, the Shi’i lost their respect, and with the exception of a few, were targeted by Yazid and his successors as Caliphs.
The main reason for Shi’i ideology is the inevitability of the Caliphate following Ali In the following few centuries, the cause of the Shi’i attracted many supporters from those who were discontented within the Caliphate, usually for those of non- Arab origin, and who were considered to be second-class citizens.
The more significant aspect was the fact that the cause of the Shi’i as a rallying place for rebellions, protests and rebellions. In addition to many failed revolts The Shi’i also played key parts in ending the Ummawiyys dynasty as well as the Shi’i Buwayhid dynasty, the Persian Dynasty was the ruler of the Abbasid Caliphate for more than 100 years. Rivalries of those of Baghdad Caliphate as well as the Fatimid Dynasty,
which was first located in Tunis and later Egypt as well as later in the Maghreb. Almohads within the Maghreb were all Shi’i. Most significantly than there was the Nizari Cult of the Assassins, established by Hasan Sabah and centered at Alamut, the Alamut mountain Fortress Alamut was a terror to as well Christian as well as Muslim officials in the Crusades and also gave Europe the term “assassin” (corruption of Hashish and was used to perform their rituals).
However the fortunes of Shi’i were extremely uncertain prior to their status as the official religion of the Safavid Dynasty in Persia during the sixteenth century. From then on the Twelver Shi’i enjoyed significant protection, support and funds through The Persian government, as well as significant theological centres were constructed within Esfahan, Najaf, Qom and Mashad. It was particularly in the 16th century when the Twelver Shi’i emerged as the most dominant sect of Shi’i and has developed a distinct style of life in comparison to those of the Sunni majoritarians.
It was also from around the year 16th that this Twelver cause has gained an unwavering adherence to Iranian foreign policy and foreign policy, with Twelver minorities in search of Iran for help and Iran considering the Twelvers’ overseas as its customers.
In the beginning of the decades of the Islamic period the Alid’s descendants and the Alid’s were considered suitable candidates to become the leaders of the Shi’i however as time passed, it became more essential for the leader of the Shi’i to be descendents of Ali through Husayn according to a predetermined line.
Contrary to the Sunni the Shi’i typically employ”imam” to refer only to Imam for only Ali and the descendents of his who were the leaders of the Shi’i group. The biggest divide between Shi’is today is between those who recognize 12 Imams, referred to as Twelvers, and those who acknowledge 7Imams, also known as Seveners or, more typically, Ismailis after Ismail the seventh Imam, and Zayyidi who do not agree with the fourth Imam and accept the authority of any Alid who is educated and is able to assert his rule with the use of force.
One of the most significant features of the Twelver Shi’i faith is the belief in returning of the final Imam, also known as Mahdi. Mahdi and who is expected to guide believers in establishing Shi’i beliefs on Islam to prepare for Judgement Day.
Other aspects that have roots within Judeo and Christian customs include the emphasis on the sufferings of martyrs (rawda Kani) and the exultation of martyrdom as a whole as well as the practice of self-flagelation within rituals of worship and the celebration of 10 days culminating with the events that occur in Karbala (ta’ziya) which is the most important event on the Shi’i calendar .
They bear striking resemblance to the passion of Christ. One of the Shi’i new feature is the permissible practice of pragmatic dissimulation (taqiyya) or the rejection of religion in public while retaining the faith in private. Another innovative idea is the concept that a the concept of temporary wedding (mut’a) which is a system in where a contract of marriage may be made for a specified duration, each that spans between one year and 99.
A woman who is entering into the mut’a receives a specific amount. According to certain Shi’i customs, a man who performs four mut’as has assured of a place in Paradise. After the Iranian revolution, the practice of mut’a came back as part of the entire Shi’i Muslim ritual.
While the Sunni regard the Shi’i as pioneers, who introduce novel and unconventional elements into Islam The Shi’i see themselves as most fundamentalists in Islam through their continued authority of Muhammad’s family. This issue can be understood within the context of the manner in which early Muslims sought guidance on issues that were not specifically covered within the Koran.
The Shi’i relied on opinions of their Imams who, as descendants from Muhammad or Ali were believed to have more in common with the divine. The Sunni were influenced by traditions that were rooted on theological and legal schools and that incorporated analogies drawn in The Koran and Hadith as well as Theologians’ consensus, where analogies were unattainable.
The four Imams that are accepted by the majority of current branches of Shi’i Islam include Ali, Hassan, Husayn Husayn, Ali and Ali Zayn l’Abidin. They are the Zayyidi from northern Yemen also acknowledge as Ali Zayn the son of Ali l’Abidin Zayyid following which they are able to recognize a myriad of Imams at different periods and locations. The most notable lineage of Imams was established by the Imams of Yemen around 893 AD and continued up to the 60’s.
There are two kinds of Ismailis. Ismailis and Twelvers both acknowledge Muhammad al Baqir, and Jafar as Sadiq and they recognize that the Ismailis acknowledge the son of Jafar, Ismail. The different Ismaili traditions also recognize various Imams’ lineages that extend into the present.
The Twelvers continue to follow Musa al Kazim, Ali ar Rida, Muhammad at Taqi, Ali al Hadi, Hassan al Askari, and Muhammad al Mahdi, their final Imam who they believe is hidden. The Twelver Shi’i also are often referred to as Rafidi, Jafari, Mutawahi, Qizilbash, Imami, Ithna Ashari, and al Khassa. A few offshoots of Shi’i Islam comprise Shi’i Islam, such as the Druze, Nusayri, and the Baha’i.

Ibadi
Branches of Islam – Another less well-known branch within Islam includes Ibadi. Ibadi is a denomination that predates Sunni as well as Shi’a as it is believed to be to be a extremely orthodox form of Islam. They also share their Shi’a conviction that God will not reveal himself in the event of Judgment Day. In contrast to Sunni and Shi’a Ibadi, Ibadi are of the belief they believe that the Muslim community is able to rule itself without the need for a leader. Ibadi differs from Shi’a in the sense that they don’t believe that the Muslim leader must be an ancestor of the tribe of Muhammad, the Quraysh. Seventy five percent of the population from Oman are Ibadis.
Ahmadiyya
The new denomination is more recent than the prior. The followers of Ahmadiyya don’t recognize or accept the Muhammad Peace Be With Him as the final prophet. It has its origins in the teachings by Mirza Ghulam Ahmad (1835-1908) who was their prophet. The followers of his believed that he was appointed by God as the person who would renew Islam. They have similar beliefs to Sunni and are also adamant about that the Qur’an as their sacred text. The most significant number of Ahmadiyya are found in West as well as East Africa, Indonesia and South Asia.

Sufism
Branches of Islam -Most Sufis adhere to the Islam guidance as outlined by Ali Muhammad, the successor of Muhammad according to the Shi’a. While it isn’t technically a religion that is part of Islam, Sufism is an Islamic doctrine that is focused on the cleansing of the inner self.
Sufis believe that people may experience a connection with God through the emotional and intuitive capabilities that Sufis develop through their learning. The experience doesn’t have to occur in Paradise but it can be experienced through the real world. Turkey along with Persia are both considered to be centers for Sufism but it also reaches Greece, Albania, and Macedonia as well as other countries.
Strength Of Beliefs
While it’s not a complete list of all the varieties of Islam The earlier denominations are among the most popular. Islam is a long-standing religion and one of the biggest worldwide and full of intricate rituals and beliefs. It doesn’t matter what religion you follow, Islams believe that the goal of all humans is to worship and live for God in hopes that one day they will get into Paradise.

Suggested Read: Dua Leaving House, Dua of Forgiveness, Dua of Taraweeh, Dua of Musa Alayhi’salam, Dua For Success, Dua For Marriage , Dua For Rain, Dua For Parents, Powerful Dua and Dua For The Sick
CONCLUSION
Major Branches Of Islam – Similarities And Differences
| Rank | Major Branches Of Islam | Estimated Global Adherents |
| 1 | Sunni | 1.39 billion |
| 2 | Shi’a | 200 million |
| 3 | Ahmadiyya | 15 million |
| 4 | Ibadi | 3 million |
| 5 | Sufism | Widely Disputed |










